LIFE WITH ICP.Problems and Solutions.Treatment modalities
Infantile cerebral paralysis occupies one of the leading places in the structure of chronic illnesses of children and adults all over the world and tends to increase the prevalence.
|
Deputy Chief Director in the “New Medical Technology's Center” Ltd, Traumatologist-orthopedist, Candidate of Medical Science |
There are more than 15 million people suffering from the ICP in the world. The plenty of causes of illness and the complexity of the pathogenesis complicate treatment rates. That’s why the infantile cerebral paralysis is on the first place among other nervous system illnesses leading to invalidity. Disturbance of impellent functions is the special feature of this disease. Because of rasping impellent disorders 80% of patients with ICP need assistance, that is why 75% of mothers have to leave work. This big group of population is banished out of normal life. The main object for doctors is to use all the possibilities to improve the health of the patients with ICP and, in particular, to raise their movement functions. Impellent act is formed with the participation both central structures (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral (spinal nerves, muscles). Raised muscle tone, blood supply disturbance and other factors cause dystrophic process in skeletal muscles. The dystrophy leads to death of a part of muscle fibers and to the substitution of these fibers by connective tissue. So fibrous scars which cause restriction of movements and regional pain syndrome (in connection with the growth of a child and scar tension) are formed. Pain syndrome promotes formation of the antalgic posture (at the expense of tonus rising in certain groups of muscles). The vicious circle is formed: raised tone – restriction of movements – muscle dystrophy – formation of connective cicatrix – muscular contracture with a regional pain syndrome – muscle tone rising – more pronounced restriction of movements. |
Operative intervention on pathologically modified muscular fibers is capable to break this vicious circle. Discission of fibrous cicatrix in a muscle eliminates regional pain syndrome and pathological tonus caused by it, remained muscular fibers have an opportunity to contract and to stretch normally – muscle function and its blood supply improves. Consequently, remained muscular fibers expand, their contractility improves. This leads to the increase of amplitude of movements, to the increase of muscle bulk and to the rise of muscle strength. During the operation it is important not to injure normal muscle fibers which side pathologically changed fibers. This result can be reached by application of special cutting instruments and by exact actions of the surgeon. Surgical instrument allow operating without big skin incisions. These operative interventions only on pathologically changed muscular fibers allow making it without applying plaster immobilization in the postoperative period and activating the patient soon (on the 3rd-4th day after operation).
Consequently, remained muscular fibers expand, their contractility improves.
This leads to the increase of amplitude of movements, to the increase of muscle bulk and to the rise of muscle strength
Surgical indications:
- presence of organic muscular contractures and myofascial pain syndrome, which cause permanent disability of muscular functions.
Contraindication to surgery:
- presence of malformation and chronic diseases at the phase of decompensation;
- acute infectious and somatic diseases, as well as exacerbation of chronic diseases, including decubation;
- anesthesia intolerance;
- presence of skin and soft tissue injuries, inflammatory diseases;
- diseases accompanied by excessive bleeding;
- conditions after convulsive attacks: after “petit mal” - not earlier than in 3 months, after “generalized” – not earlier than in 6 month, after epileptic seizure – not earlier than in 12 months;
- condition after introduction of Botox – not earlier than in 6 months;
- condition after vaccination – not earlier than in a month.
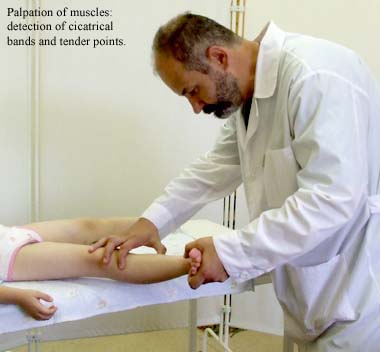
Low-traumatic operations allow eliminating up to 12-14 muscular contractures within one step. Often patients who suffer from infantile cerebral paralysis have got a lot of cicatrical contractions and it is impossible to eliminate all of them during one operating intervention. Then surgical treatment should be made in several steps. The main target of each complex of operations is to increase patients’ motion activity. For this purpose before each surgical attack the surgeon defines contractures which must be eliminated at that stage. It should be emphasized: the surgeon should aspire to the result which is 100% predictable. For this purpose he should verify the plan of surgical intervention: firstly, at the moment of observation over the patients’ movements and postures, the orthopedist identifies muscles which are mostly struck with disease; secondly, during muscles’ examination and and palpation he reveals cicatrical bands and tender points; thirdly, immediately before surgical attack when the patient is under anesthesia, at the time of muscles relaxation ( when cicatrical bands are well-marked) – the orthopedist palpates muscles again, checking evolved plan of surgical intervention.
|
A doctor, like a sculptor, should foresee the result of the operation, lay down a blue-print of rehabilitation actions with obligatory control of patients’ achievements and he should predict: when and on what muscles next stage of surgical intervention must be made. Surgeries in early stage of muscular contractures before nascence of fixed contractures and deformation of joints are most effective. That’s why it is preferably to begin surgical treatment at the age of 3-5. It’s worth noting that well-timed surgical intervention promotes not only the increase of range of motions of a child but it also promotes improvement in general state of health, growth, nurture of mind (as a result of increase in mobility and minimization of pathological impulsation from the muscles which underwent surgery). |
Movements and postures of the patient show the muscles affected by disease. |
For patients who suffer from infantile cerebral paralysis it is essential to move each hour at least for several minutes.
Prolonged therapeutic exercises and long rest periods (>1hour) are contraindicated.
|
Palpation of muscles: detection of cicatrical bands and tender points. |
Correctly organized post-operative rehabilitation improves productivity of surgical treatment and plays a very important role in improvement of impellent possibilities of a patient. Within a month after surgery a patient gradually enlarge his motor abilities to the level, that was available before surgery. As the pain syndrome is falling, exercise therapy and passive gymnastics are recommended to the patient. For those, whose range of motions in joints is limited because of permanent pathological postures, passive gymnastics is essential. Little by little patients should pass to passive-active and active gymnastics. It should be noted that the main target of therapeutic exercise is to stimulate various motor activity, without causing fatigue. For this purpose it is possible to use various physical exercises and training simulators which are adapted for possibilities of ICP patients. Activity duration should correspond to a physical condition of the patient: from 10 to 30-40 minutes). If there are some indications of weariness, exercises should be stopped. After relaxation exercises should be repeated. The muscles have adequate exercise stress that promotes development of physical mass and muscular strength of the patient. |
During post-operative rehabilitation the following is not recommended:
- stenuous exercises, abrupt movements, fixed postures;
- intensive muscle stretching and prelums during massage or gymnastics;
- general and local actions of high (above 40 degrees) and low (below 20 degrees) temperatures;
- prolonged immobilization of the extremities and the trunk.
For patients who suffer from infantile cerebral paralysis it is essential to move each hour at least for several minutes. Prolonged therapeutic exercises and long rest periods (>1hour) are contraindicated. The doctor should control the rehabilitation process in order to make adjustments in time and to understand when the next stage of surgical treatment should be performed. Meeting all the above-mentioned conditions will allow low-traumatic surgeries on pathologically changed muscular fibers to contribute the treatment of the patients suffering from ICP and to raise the rehabilitation process on a whole new level. Improvement of impellent functions of every patient can and should be reached.